Stem
cells are pluripotent cells with the ability to self-replicate. Under certain
conditions, it can differentiate into a variety of functional cells. Stem
cells are classified as embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and somatic Stem cells according
to their stage of development. According to their developmental potential, stem
cells are divided into three categories: totipotent stem cells (TSC), pluripotent
stem cells and unipotent stem cells. Stem cells are insufficiently
differentiated and immature cells with the potential to regenerate various
tissues and organs. They are called Versatile Cells in the medical
field.
Market Status and Forecast of Global and Korean Stem Cell
banking Industry
After
a period of development, the industry has entered the mature period. Globally,
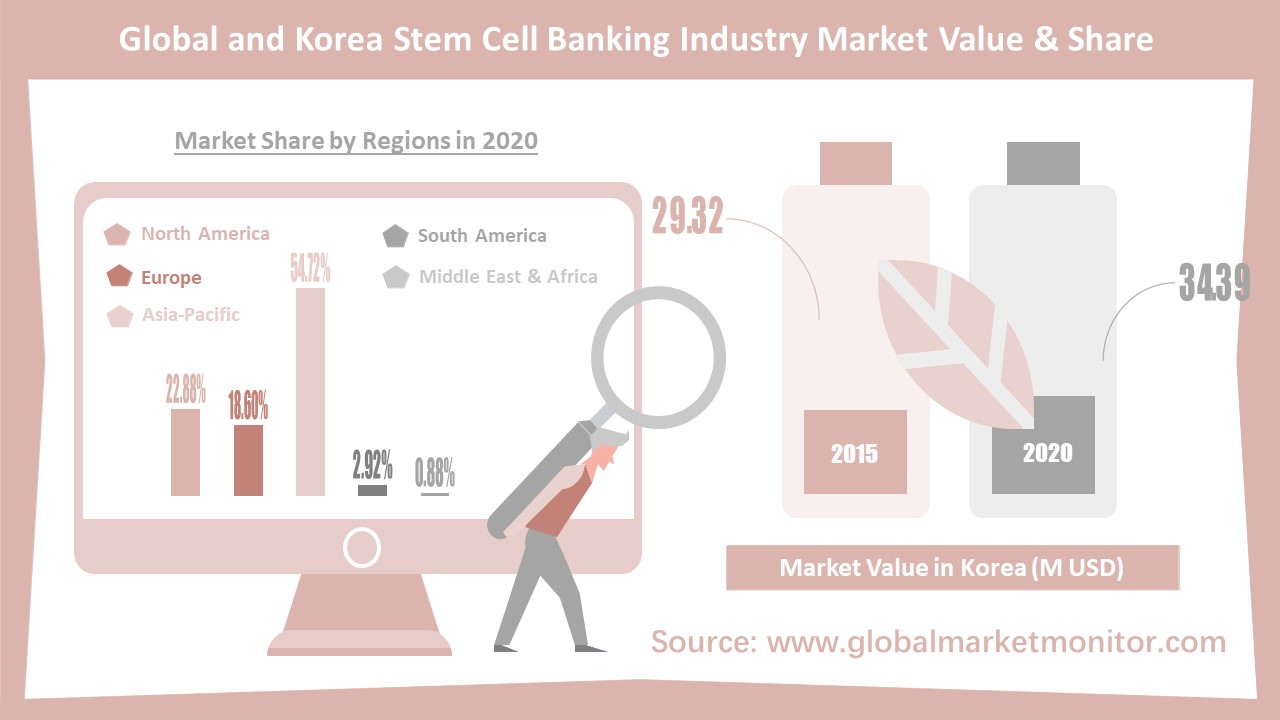
the Asia-Pacific region is the largest revenue market for the stem cell banking
industry. In 2020, the market revenue of
the industry in the Asia-pacific region was $756.52 million, accounting for
46.21% of the global market share. North America and Europe ranked second and
third with market shares of 28.73% and 21.08% respectively. South America and Middle East and Africa
accounted for 3.01% and 0.98% of the market, respectively. In addition, the
future development trend of the industry in the Asia-pacific region is also
good, and it is predicted that the industry will continue to develop rapidly in
the next five years. It is estimated that by 2025, the market share of the
region in the global market will reach 54.72%.
Data
show that the total market revenue of the global stem cell bank industry in
2015 was $1295.15 million. The industry developed steadily from 2015 to 2020,
and the total market value reached $1637.29 million by 2020. Based on this
data, and combined with the industry development law, we carried out a series
of function operations, scientific derivation of the next five years of data. Finally,
it is predicted that the annual value of the global stem cell industry will
continue to rise during 2021 to 2025, and will grow to $2446.74 million in
2025.
View the full TOC at: https://www.globalmarketmonitor.com/reports/762705-stem-cell-banking-market-report.html
The Impact of the Epidemic on the Global Stem Cell Banking
Industry and its Future Development Trend
Stem
cell technology has long been used to treat infectious diseases and
complications. Previous attempts to treat H7N9 bird flu using stem cell
technology have worked well. Therefore, a number of medical and scientific
institutions in China have launched research on stem cell treatment of COVID-19.
Stem cells hold promise for repairing lung tissue damage that puts critically-ill
patients at risk of death and sequelae. For the treatment of COVID-19, the
existing clinical application is particularly effective in rescuing critically
ill cases. The mechanisms of action are multifold, including direct contact of
stem cells with target cells, paracrine action, regulation of immune function,
inhibition of inflammation, reduction of alveolar epithelial cell death, and
promotion of lung tissue repair.
Although
it will take some time to become widely available, stem cell technology creates
opportunities and options for overcoming COVID-19 or some relatively dangerous
diseases. COVID-19 patients are mainly concentrated in the elderly, especially
those with chronic diseases, and the main susceptibility factors are decreased
body function and weakened immunity. As a result, they are more susceptible to COVID-19,
and their illness is relatively accelerated and more severe. Stem cells play a
key role in treating chronic diseases or COVID-19 pneumonia. As a result, the
COVID-19 pandemic has boosted the use of stem cells and is largely driving the
growth of the market.
In
addition, although the living standards and quality have improved significantly
in recent years, there are more and more chronic diseases in the world, and the
proportion of deaths caused by chronic diseases is also increasing. Chronic
diseases have long course, complicated etiology and they are difficult to treat.
Stem cell therapies have great potential to treat a range of common chronic
diseases, including diabetes, heart disease (myocardial infarction),
Parkinsons disease, spinal cord injury, arthritis, Amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis, cancer, blood and immune system diseases. Until a few years ago, there was no cure or
effective treatment for these diseases. The benefits of stem cells include
reversing diseases such as Parkinsons by growing new, healthy, functioning
brain cells; Repairing and regenerate tissue and muscle damaged by heart
disease; Addressing genetic defects by introducing normal cells; Reducing the
mortality rate of patients waiting for organ transplants by regenerating
healthy cells and tissue as a replacement for donated organs. Therefore, given
the effectiveness of stem cells in treating chronic diseases, the rising
incidence of chronic diseases is an opportunity for the stem cell banking
industry.
However, cell, tissue and biobank banks incur significant expenses in sample processing, quality testing, and sample storage and storage, not including the purchase and maintenance of high-priced instruments, reagents and consumables, which undoubtedly impose high operating costs on service providers. In addition, the increasingly strict and mandatory high ethical standards and regulatory requirements related to stem cell preservation and storage, as well as the expensive licensing and approval procedures for the establishment of stem cell banks in developed countries, are expected to further increase the overall operating costs of stem cell bank service providers, which brings some challenges to the development of stem cell bank market.
View the full TOC at: https://www.globalmarketmonitor.com/reports/762705-stem-cell-banking-market-report.html
We provide more professional and intelligent market reports to complement your business decisions.